SECTORS
Smart Cities
Smart public transport networks, water supply and waste disposal facilities efficiency, development of urban green mobility projects, air and pollution monitoring, care of the territory for the prevention of extreme climatic events and hydrogeological risk: these are just some of the technologies that SmartMe can design for smart cities and that can concern, just to name a few, traffic, tourism, environment, school, safety of citizens.
Starting a real smart city project requires a thorough knowledge of technologies and tools of IoT and AI but also the ability to manage and analyze big data through a platform that allows real-time monitoring. Many of our devices are already present in many municipalities, large and small throughout Italy, representing a sustainable and smart choice for residential areas digital transformation.

Industry 4.0
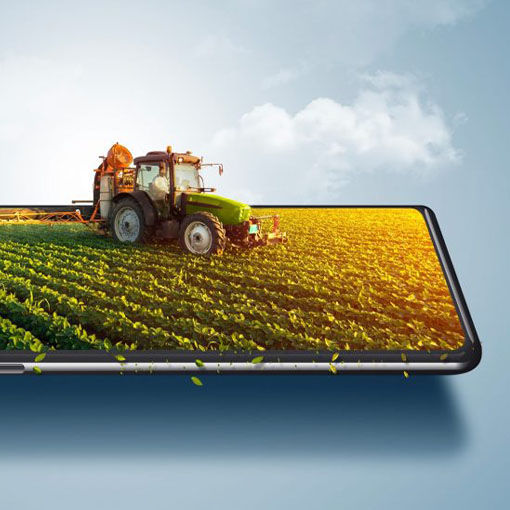
Digital Farming
SmartMe works alongside companies in the agricultural sector intending to adopt those digital tools and skills encouraging the transition to so-called 4.0 agriculture in full respect of energy and environmental sustainability. More than others, agricultural enterprises are called to adopt these innovations. Climate change is increasingly putting the sector to the test, so precision farming has become the most effective tool to tackle these problems by optimising, for example, irrigation activity or the collection process, through a 360° control infrastructure.
From agronomy to meteorology, from crop defence to agro-mechanical processing: the application of IoT solutions and preventive and predictive maintenance to agricultural processes aims to ensure sustainable management of resources, producing more efficiently and consuming less. It is possible to create in this way a circular infrastructure that allowing to record data (of the weather, of the ground, of the status of the machines etc.), store them in the cloud and make them accessible in a shared way on the network, and then process them with artificial intelligence algorithms, for autonomous monitoring in real time. The benefits can be countless: reduction of the operating costs of the machinery, preventive maintenance and automation of the same, improvement of the quality of the final product, Control and monitoring along the entire production line and waste control, as well as data tracking and data storage for the interpretation of information.




